Introduction
Acetates are everywhere! From your favorite pair of glasses to the nail polish on your shelf, these compounds are an essential part of daily life. But what exactly are acetates? Why are they so important? Let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know about these versatile substances.
What Are Acetates?
Definition and Basic Explanation
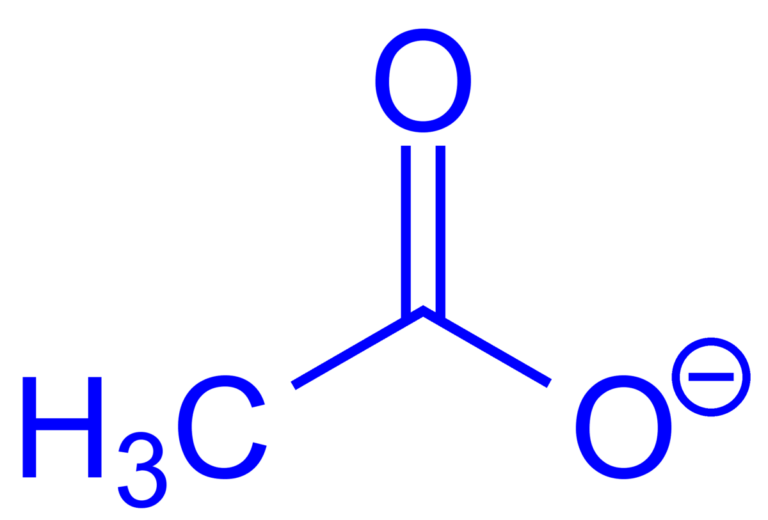
Acetates are chemical compounds derived from acetic acid. They can be organic or inorganic and are commonly used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and plastics. In simple terms, they are salts or esters of acetic acid, playing a key role in both nature and industry.
Types of Acetates
Organic vs. Inorganic Acetates
- Organic Acetates: These are primarily used in the production of synthetic materials like plastics and textiles.
- Inorganic Acetates: Often found in industrial chemicals, metal treatments, and laboratory applications.
Common Acetates in Daily Life
- Sodium acetate (used in heating pads)
- Calcium acetate (food additive and medicine)
- Cellulose acetate (used in textiles and eyewear frames)
Chemical Structure of Acetates
Composition and Molecular Formula
The general formula for acetate is C2H3O2−. When combined with metals or organic compounds, it forms salts or esters with different properties.
How Acetates Are Formed
Acetates are typically formed through the reaction of acetic acid with bases, alcohols, or metals.
Common Uses of Acetates
Industrial Applications
Acetates are widely used in manufacturing plastics, adhesives, and coatings.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Uses
Certain acetates, like zinc acetate and calcium acetate, are used in medicines and dietary supplements.
Food and Beverage Industry
Calcium acetate acts as a preservative and thickening agent in food products.
Textile and Fashion Industry
Cellulose acetate is a key material in producing fabrics and eyewear.
Acetates in Everyday Products
Eyewear and Plastic Products
Many high-end glasses frames are made of cellulose acetate due to its durability and flexibility.
Nail Polish and Beauty Products
Ethyl acetate is a common solvent in nail polish and perfumes.
Adhesives and Coatings
Acetates improve the performance of paints, varnishes, and adhesives.
Benefits of Acetates
- Versatility: Used across multiple industries
- Biodegradability: Some forms break down naturally
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable production and use
Potential Risks and Safety Concerns
Health Hazards
Some acetate compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large amounts.
Environmental Impact
Non-biodegradable acetates contribute to pollution if not disposed of properly.
How Acetates Are Manufactured
Acetates are typically produced in laboratories and industrial settings using chemical reactions involving acetic acid and other compounds.
Acetates in Science and Research
Scientists continuously explore new uses for acetates in medicine, sustainable packaging, and nanotechnology.
How to Properly Handle Acetates
Storage Guidelines
Keep in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Safe Usage Tips
Use protective gear when handling concentrated acetate solutions.
Regulations and Standards for Acetates
Acetates are regulated by agencies like the FDA and EPA to ensure their safe use in food, medicine, and industrial applications.
Acetates and Sustainability
Many companies are developing eco-friendly acetate alternatives to reduce environmental harm.
Interesting Facts About Acetates
- Some acetate compounds are used in photographic films.
- Sodium acetate is used in instant hot packs.
- Cellulose acetate is biodegradable, unlike many synthetic plastics.
Conclusion
Acetates are an essential part of our modern world, used in everything from textiles to medicine. While they offer many benefits, responsible use and disposal are crucial for environmental sustainability.
FAQs
1. Are acetates safe for human use?
Yes, most acetates are safe when used as intended. However, some can be toxic in high concentrations.
2. What are the most common acetate products?
Glasses frames, nail polish remover, and heating pads are some of the most common products containing acetates.
3. Are acetates biodegradable?
Some, like cellulose acetate, are biodegradable, while others may not be.
4. How are acetates different from acetone?
Acetates are salts or esters of acetic acid, whereas acetone is a ketone used primarily as a solvent.
5. Can acetates be recycled?
Certain acetate materials, like cellulose acetate, can be recycled, but it depends on local recycling facilities.